Accessibility: Preparing Your Site Structure
8 min
In this article
- Recommendations for preparing text
- Adding HTML tags to text from your editor
- Adding HTML tags to text from the Accessibility Wizard
Your site's hierarchy (its structure) helps web browsers and screen readers understand how the site content should be organized. You can add HTML tags to site text to indicate its place in the site's order and provide a clear experience for visitors.
Good to know:
Webpage content is "read" by the DOM order of your site pages. You can check this order and adjust it if needed. Learn more about organizing your site's order.
Recommendations for preparing text
We recommend keeping the following guidelines in mind when preparing site text:
- Use HTML tags for your text: Every page should have an H1 heading, and following that, the HTML tags on each page should be sequential. For example, if the main heading on the page is an H1 tag, the subtitle should be H2, and so on. This is so visitors with visual impairments can toggle through your content in a logical order.
- The headings should be descriptive: Think of the headings as labels for the text below (this is also important for SEO).
- Spacing is important: While editing your text, if you want to break a heading into multiple lines, use the Shift + Enter keys to insert a line break, instead of Enter which creates a new heading element on each line.
- Add headings to the page body: H1s added to a site header will appear on all pages where the header is displayed. We therefore recommend adding headings to the page body instead.
Tip: If you have a one-page site with no additional pages, you can ignore this recommendation.
Adding HTML tags to text from your editor
Add HTML tags to site text to define its hierarchy. If you're building a site with the Wix Editor, you can select the tag from the text settings. If you're working with the Studio Editor, you can find it in the Inspector panel. The option is also available in the design options of text in Wix Harmony Editor.
Wix Editor
Studio Editor
Wix Harmony Editor
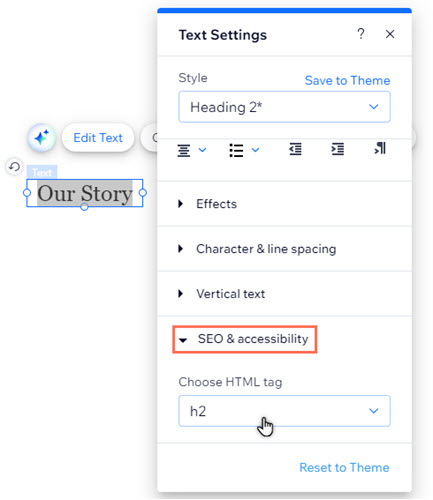
- Select the relevant text in your editor.
- Select Edit Text.
- Select SEO & Accessibility.
- Choose an HTML tag from the drop-down menu.
Adding HTML tags to text from the Accessibility Wizard
Scan a site with the Accessibility Wizard to find and adjust tags on your text elements. The wizard is available in all of our site builders, so you can improve the accessibility of any site you're working on.
With most text, you can make changes within the wizard itself. However, some text elements (e.g. app text) are not currently fully integrated with the wizard, and may need to be manually adjusted.
Wix Editor
Studio Editor
Wix Harmony Editor
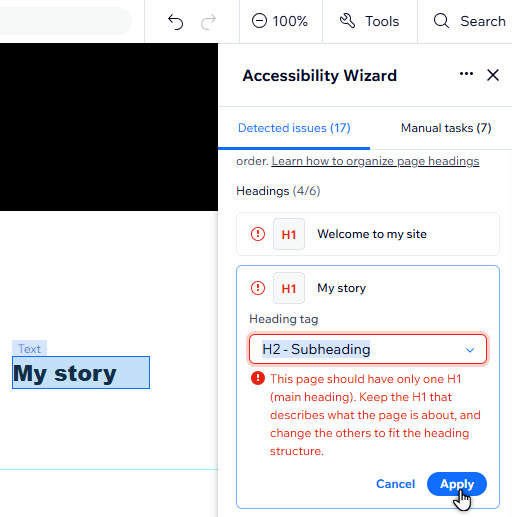
- Go to your editor.
- Click Settings at the top.
- Select Accessibility Wizard.
- Select Scan Site.
- Click the Detected issues tab.
- Select the relevant page.
- Click Organize heading structure.
- Select the relevant text element.
- Depending on whether the text is supported in the wizard, follow one of the below methods:
Choose the tag in the wizard
Manually adjust the tag
Next step:
Go back to the Accessibility Checklist to continue improving your site for accessibility.